When venturing into the world of corporate XR, the hardware is a very important piece of the puzzle as the choice of headset you use will determine the quality of your experience. High end headsets require a powerful computer to run, while lower end headsets like the Oculus Quest are standalone devices.
In addition, there are multiple extras, ranging from the basic hand controllers to more complex equipment like treadmills or haptic gloves that react to virtual stimuli. These all add to the level of immersion you can experience in XR.

Oculus Quest for Business
Oculus Quest is Facebook’s first standalone headset that offers 6DOF tracking on both the head and hands. That means that the headset has the same full tracking capabilities typically reserved for high-end VR headsets that are hooked up to a computer. Because Quest has full 6DOF tracking, it opens the door to significantly more immersive and interactive content than other standalone headsets. Given that it’s a “standalone”, Quest’s biggest advantage is its low friction experience.
PROS
- Low friction experience
- Excellent VR for a standalone device
- Reasonable price
CONS
- Limited graphics capability compared to other headsets
- Heavy on the face

HTC Vive Pro / Vive for business
With a resolution of 2880 x 1600, the HTC Vive Pro offers amazing image quality. If graphics are important this headset is a safe bet. A nose guard keeps light leakage to a minimum. The kit comes with lighthouses that need to be installed in an elevated position for the headset to work. These lighthouses are sensitive to other light sources like the sun’s rays and therefore need to be placed in a setting with minimum natural light.
PROS
- Blocks most outside light
- Comes with headphones
- High resolution display
CONS
- Complicated setup
- Headphones tend to crackle
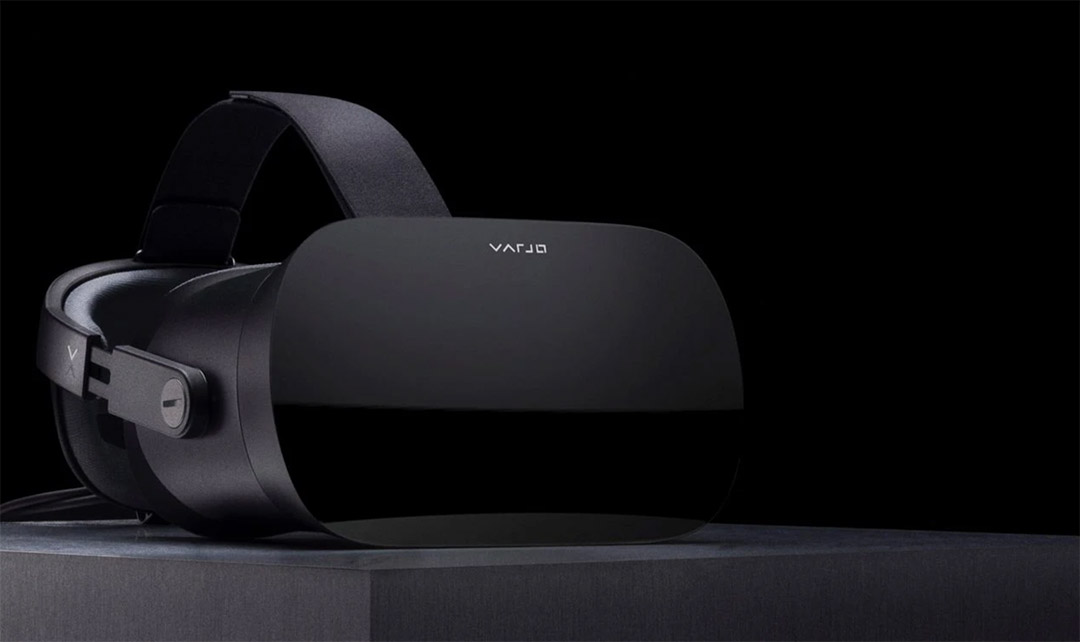

Varjo VR-2
The makers of Varjo VR-2 pride themselves on delivering “human eye-resolution”. The target market for this headset is industrial settings where clients require the highest visual fidelity possible (current clients include Audi and NASA). The Varjo VR-2 features eye tracking technology that allows clients to analyze users’ gaze for research, training, simulation and industrial design for example. The VR-2 Pro also features hand tracking. No need for bulky controllers. Users utilize their hands just as they would in real life.
PROS
- Extremely high resolution
- Excellent eye tracking
- Hand tracking
CONS
- Very expensive

HP Reverb G2 Omnicept
The HP Reverb G2 Omnicept is raising the bar for what a VR headset should be by incorporating multiple biometric sensors to help developers and enterprises better track users’ reactions. This is of course particularly useful for companies looking to gather user data in a VR setting.
PROS
- Face recognition camera
- Heartbeat monitor
- Gaze and pupil size monitor
CONS
- Will not hit stores until next year
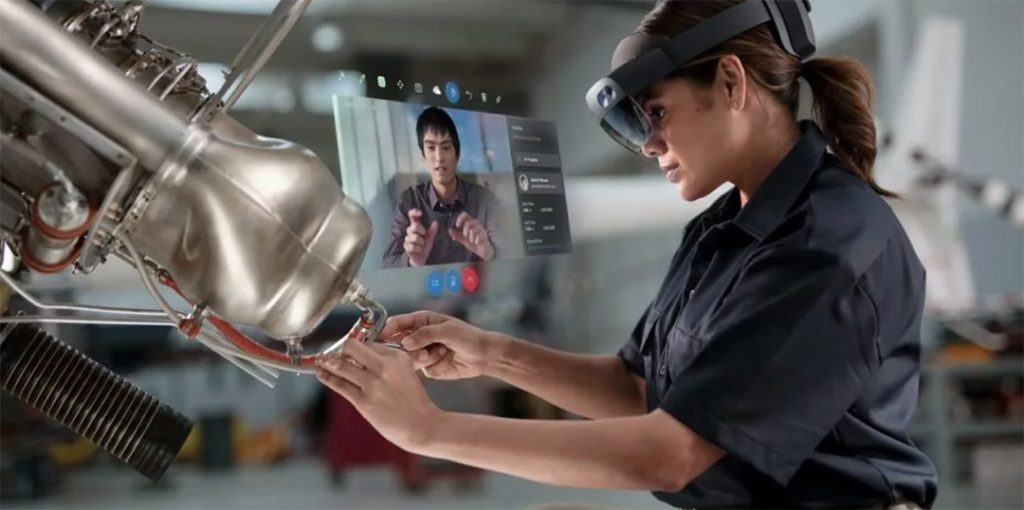

Microsoft Hololens 2
The main difference between Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality (MR) is that VR shuts out the outside world. MR overlays virtual objects within the real world. The Hololens 2 is specifically targeted towards enterprise use and Microsoft has built a solid library of use cases where the use of AR with this headset has brought massive ROI to their clients.
PROS
- Suitable for “first line workers”
- Hand tracking
CONS
- Expensive
- Limited field of view
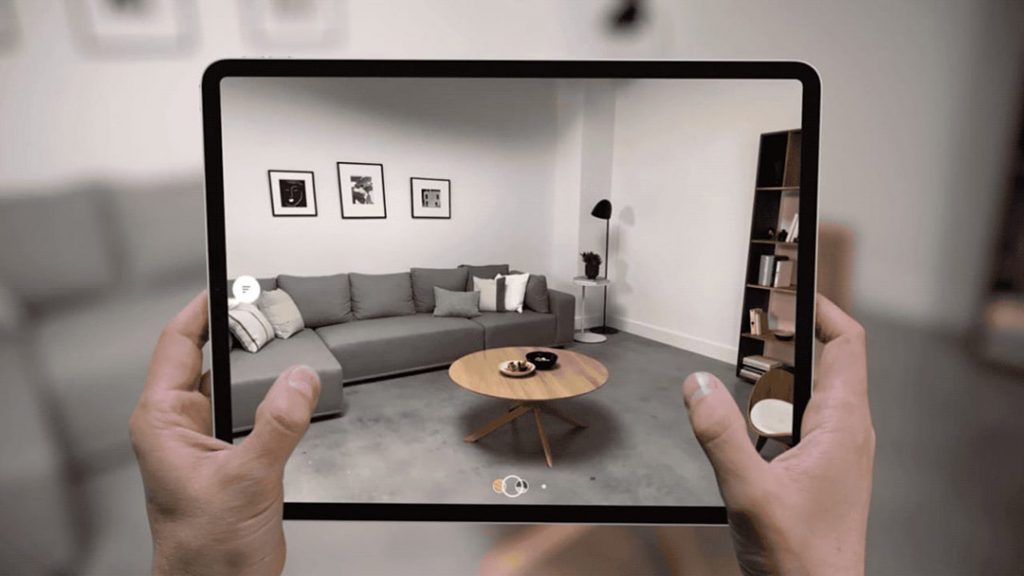

PC / Phone / Tablet
While not at all as immersive and powerful as experienced through an XR headset – it’s also completely possible to view virtual content through a PC, a phone or a tablet. This is particularly useful when working on large teams where not everybody has access to an XR headset but can still participate in the experience.
PROS
- Inclusive as anybody can see what’s going on
- Ubiquitous and accessible in corporate settings
CONS
- Lacks in immersion